Name
ST_CoverageClean — Computes a clean (edge matched, non-overlapping, gap-cleared) polygonal coverage, given a non-clean input.
Synopsis
geometry ST_CoverageClean(geometry winset geom, float8 gapMaximumWidth = 0, float8 snappingDistance = -1, text overlapMergeStrategy = 'MERGE_LONGEST_BORDER');
Descrizione
A window function which adjusts the edges of a set of valid polygonal geometries to produce a clean coverage. Cleaning involves:
-
snapping vertices and edges to remove small discrepancies and ensure common edges are identically noded
-
merging overlaps into a parent polygon
-
merging narrow gaps into adjacent polygons
gapMaximumWidth controls which gaps between polygons are merged. Gaps with width <= this distance are merged into an adjacent polygon.
snappingDistance controls snapping of vertices and edges. The default (-1) automatically determines a snapping distance based on the input extent. Set to 0.0 to turn off snapping.
overlapMergeStrategy specifies how overlaps are merged into a parent polygon:
-
MERGE_LONGEST_BORDER- merges into polygon with longest common border -
MERGE_MAX_AREA- merges into polygon with maximum area -
MERGE_MIN_AREA- merges into polygon with minimum area -
MERGE_MIN_INDEX- merges into polygon with smallest input index (defined by order of input polygons)
The result is a clean polygonal coverage that will pass validation by ST_CoverageInvalidEdges and can be input to coverage processing functions.
![[Note]](../images/note.png)
|
|
|
To aid in determining a maximum gap width, gaps can be computed by cleaning with |
Availability: 3.6.0 - requires GEOS >= 3.14.0
Esempi
-- Populate input table CREATE TABLE example AS SELECT * FROM (VALUES (1, 'POLYGON ((10 190, 30 160, 27 134.5, 40 110, 122 47, 120 10, 10 10, 10 190))'::geometry), (2, 'POLYGON ((150 190, 10 190, 30 160, 50 140, 40 110, 50 80, 130 70, 135 111, 140 130, 140 160, 150 190))'::geometry), (3, 'POLYGON ((140 190, 190 190, 190 80, 140 80, 140 190))'::geometry), (4, 'POLYGON ((190 10, 120 10, 97 77, 160 90, 170 70, 190 80, 190 10))'::geometry) ) AS v(id, geom);
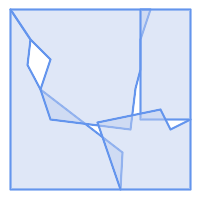
Polygons with overlaps and gaps
-- Show it is an invalid coverage SELECT ST_AsText(ST_CoverageInvalidEdges(geom) OVER ()) FROM example;
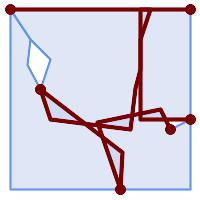
Invalid coverage edges
-- Clean the coverage, merging gaps with width <= 1 CREATE TABLE example_clean AS SELECT id, ST_CoverageClean(geom, 1) OVER () AS GEOM FROM example;
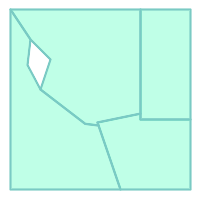
Clean polygonal coverage, with overlaps and narrow gaps removed