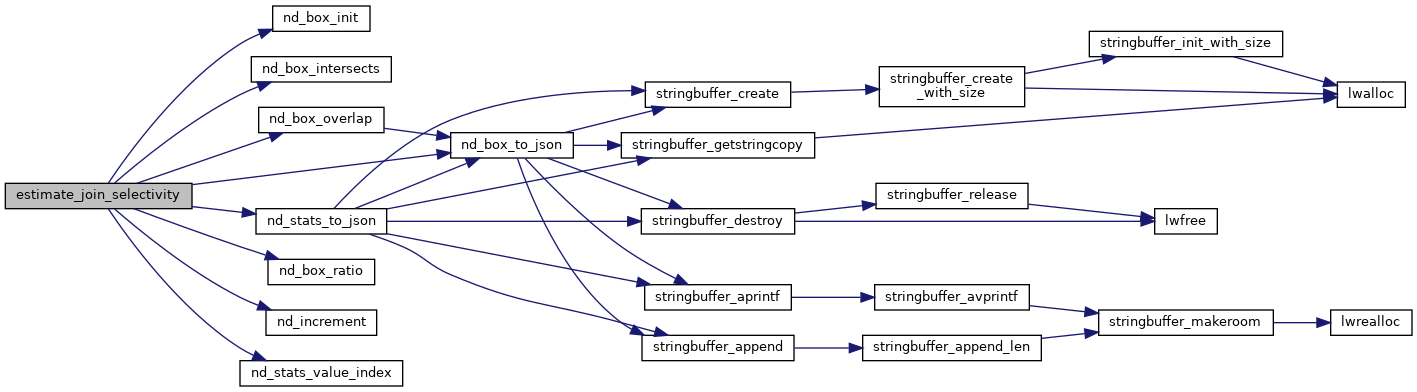
Given two statistics histograms, what is the selectivity of a join driven by the && or &&& operator?
Join selectivity is defined as the number of rows returned by the join operator divided by the number of rows that an unconstrained join would return (nrows1*nrows2).
To get the estimate of join rows, we walk through the cells of one histogram, and multiply the cell value by the proportion of the cells in the other histogram the cell overlaps: val += val1 * ( val2 * overlap_ratio )
1051 int ncells1, ncells2;
1052 int ndims1, ndims2, ndims;
1054 double ntuples_not_null1, ntuples_not_null2;
1073 if ( ! ( s1 && s2 ) )
1075 elog(NOTICE,
" estimate_join_selectivity called with null inputs");
1084 if ( ncells1 > ncells2 )
1102 ntuples_max = ntuples_not_null1 * ntuples_not_null2;
1105 ndims1 = (int)roundf(s1->
ndims);
1106 ndims2 = (int)roundf(s2->
ndims);
1107 ndims = Max(ndims1, ndims2);
1116 POSTGIS_DEBUG(3,
"relation stats do not intersect, returning 0");
1117 PG_RETURN_FLOAT8(0.0);
1126 POSTGIS_DEBUG(3,
"could not calculate overlap of relations");
1131 for ( d = 0; d < ndims1; d++ )
1133 at1[d] = ibox1.
min[d];
1136 size1[d] = (int)roundf(s1->
size[d]);
1137 cellsize1[d] = width1[d] / size1[d];
1141 for ( d = 0; d < ndims2; d++ )
1145 size2[d] = (int)roundf(s2->
size[d]);
1146 cellsize2[d] = width2[d] / size2[d];
1156 for ( d = 0; d < ndims1; d++ )
1158 nd_cell1.
min[d] = min1[d] + (at1[d]+0) * cellsize1[d];
1159 nd_cell1.
max[d] = min1[d] + (at1[d]+1) * cellsize1[d];
1166 for ( d = 0; d < ndims2; d++ )
1168 at2[d] = ibox2.
min[d];
1171 POSTGIS_DEBUGF(3,
"at1 %d,%d %s", at1[0], at1[1],
nd_box_to_json(&nd_cell1, ndims1));
1185 for ( d = 0; d < ndims2; d++ )
1187 nd_cell2.
min[d] = min2[d] + (at2[d]+0) * cellsize2[d];
1188 nd_cell2.
max[d] = min2[d] + (at2[d]+1) * cellsize2[d];
1191 POSTGIS_DEBUGF(3,
" at2 %d,%d %s", at2[0], at2[1],
nd_box_to_json(&nd_cell2, ndims2));
1194 ratio2 =
nd_box_ratio(&nd_cell1, &nd_cell2, Max(ndims1, ndims2));
1198 POSTGIS_DEBUGF(3,
" val1 %.6g val2 %.6g ratio %.6g", val1, val2, ratio2);
1199 val += val1 * (val2 * ratio2);
1206 POSTGIS_DEBUGF(3,
"val of histogram = %g", val);
1217 POSTGIS_DEBUGF(3,
"val scaled to full table size = %g", val);
1234 selectivity = val / ntuples_max;
1237 if ( isnan(selectivity) || ! isfinite(selectivity) || selectivity < 0.0 )
1241 else if ( selectivity > 1.0 )
static char * nd_stats_to_json(const ND_STATS *nd_stats)
Convert an ND_STATS to a JSON representation for external use.
static int nd_box_intersects(const ND_BOX *a, const ND_BOX *b, int ndims)
Return true if ND_BOX a overlaps b, false otherwise.
static int nd_increment(ND_IBOX *ibox, int ndims, int *counter)
Given an n-d index array (counter), and a domain to increment it in (ibox) increment it by one,...
#define ND_DIMS
The maximum number of dimensions our code can handle.
#define DEFAULT_ND_JOINSEL
#define FALLBACK_ND_SEL
More modest fallback selectivity factor.
#define FALLBACK_ND_JOINSEL
static int nd_box_init(ND_BOX *a)
Zero out an ND_BOX.
static int nd_box_overlap(const ND_STATS *nd_stats, const ND_BOX *nd_box, ND_IBOX *nd_ibox)
What stats cells overlap with this ND_BOX? Put the lowest cell addresses in ND_IBOX->min and the high...
static double nd_box_ratio(const ND_BOX *b1, const ND_BOX *b2, int ndims)
Returns the proportion of b2 that is covered by b1.
static int nd_stats_value_index(const ND_STATS *stats, int *indexes)
Given a position in the n-d histogram (i,j,k) return the position in the 1-d values array.
static char * nd_box_to_json(const ND_BOX *nd_box, int ndims)
Convert an ND_BOX to a JSON string for printing.
N-dimensional box type for calculations, to avoid doing explicit axis conversions from GBOX in all ca...
N-dimensional box index type.
N-dimensional statistics structure.